|
I'm a first-year Ph.D. student at Zhejiang University (ZJU). Previously, I got my Bachelor's degree from Nanjing University (NJU). Research interests: Robotics (Embodied AI) and Reinforcement Learning. |

|
|
|
|
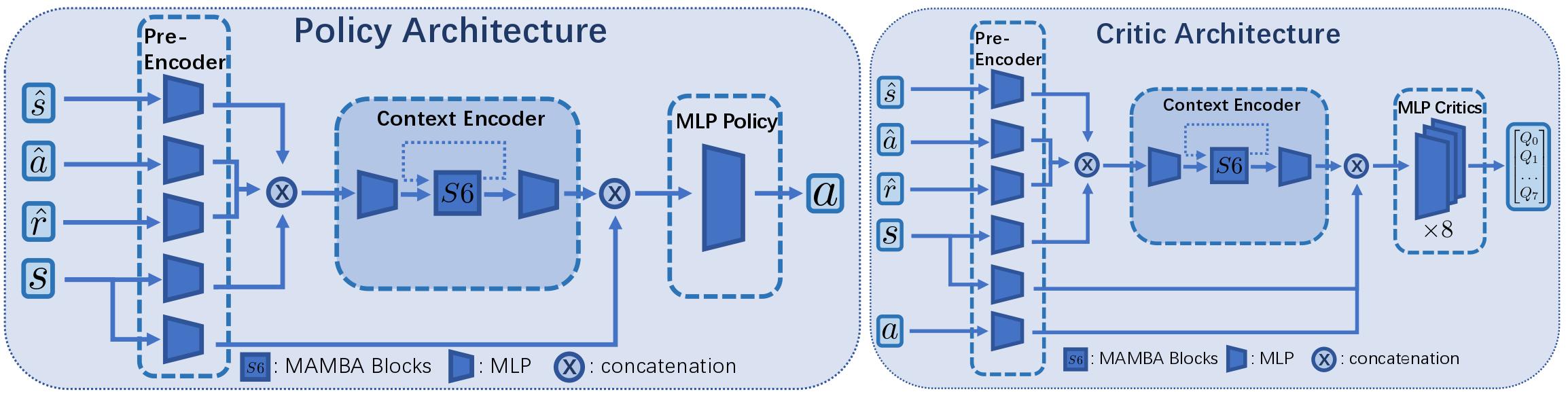
Fan-Ming Luo, Zuolin Tu, Zefang Huang, Yang Yu Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024
Real-world decision-making tasks are usually partially observable Markov
decision processes (POMDPs), where the state is not fully observable. Recent progress has
demonstrated that recurrent reinforcement learning (RL), which consists of a context encoder
based on recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for unobservable state prediction and a multilayer
perceptron (MLP) policy for decision making, can mitigate partial observability and serve as a
robust baseline for POMDP tasks. However, previous recurrent RL methods face training stability
issues due to the gradient instability of RNNs. In this paper, we propose Recurrent Off-policy
RL with Context-Encoder-Specific Learning Rate (RESeL) to tackle this issue. Specifically, RESeL
uses a lower learning rate for context encoder than other MLP layers to ensure the stability of
the former while maintaining the training efficiency of the latter. We integrate this technique
into existing off-policy RL methods, resulting in the RESeL algorithm. We evaluated RESeL in 18
POMDP tasks, including classic, meta-RL, and credit assignment scenarios, as well as five MDP
locomotion tasks. The experiments demonstrate significant improvements in training stability
with RESeL. Comparative results show that RESeL achieves notable performance improvements over
previous recurrent RL baselines in POMDP tasks, and is competitive with or even surpasses
state-of-the-art methods in MDP tasks. Further ablation studies highlight the necessity of
applying a distinct learning rate for the context encoder.
|
|
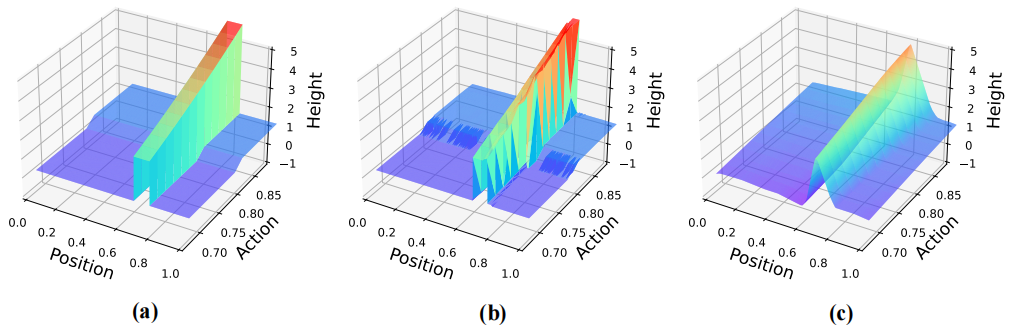
Ruifeng Chen∗, Chengxing Jia∗, Zefang Huang, Tian-Shuo Liu, Xu-Hui Liu, Yang Yu The International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2024
Learning a high-quality transition model is of great importance for sequential
decision-making tasks, especially in offline settings. Nevertheless, the complex behaviors of
transition dynamics in real-world environments pose challenges for the standard forward models
because of their inductive bias towards smooth regressors, conflicting with the inherent nature
of transitions such as discontinuity or large curvature. In this work, we propose to model the
transition probability implicitly through a scalar-value energy function, which enables not only
flexible distribution prediction but also capturing complex transition behaviors. The
Energy-based Transition Models (ETM) are shown to accurately fit the discontinuous transition
functions and better generalize to out-of-distribution transition data. Furthermore, we
demonstrate that energy-based transition models improve the evaluation accuracy and
significantly outperform other off-policy evaluation methods in DOPE benchmark. Finally, we show
that energy-based transition models also benefit reinforcement learning and outperform prior
offline RL algorithms in D4RL Gym-Mujoco tasks.
|
|
|
|
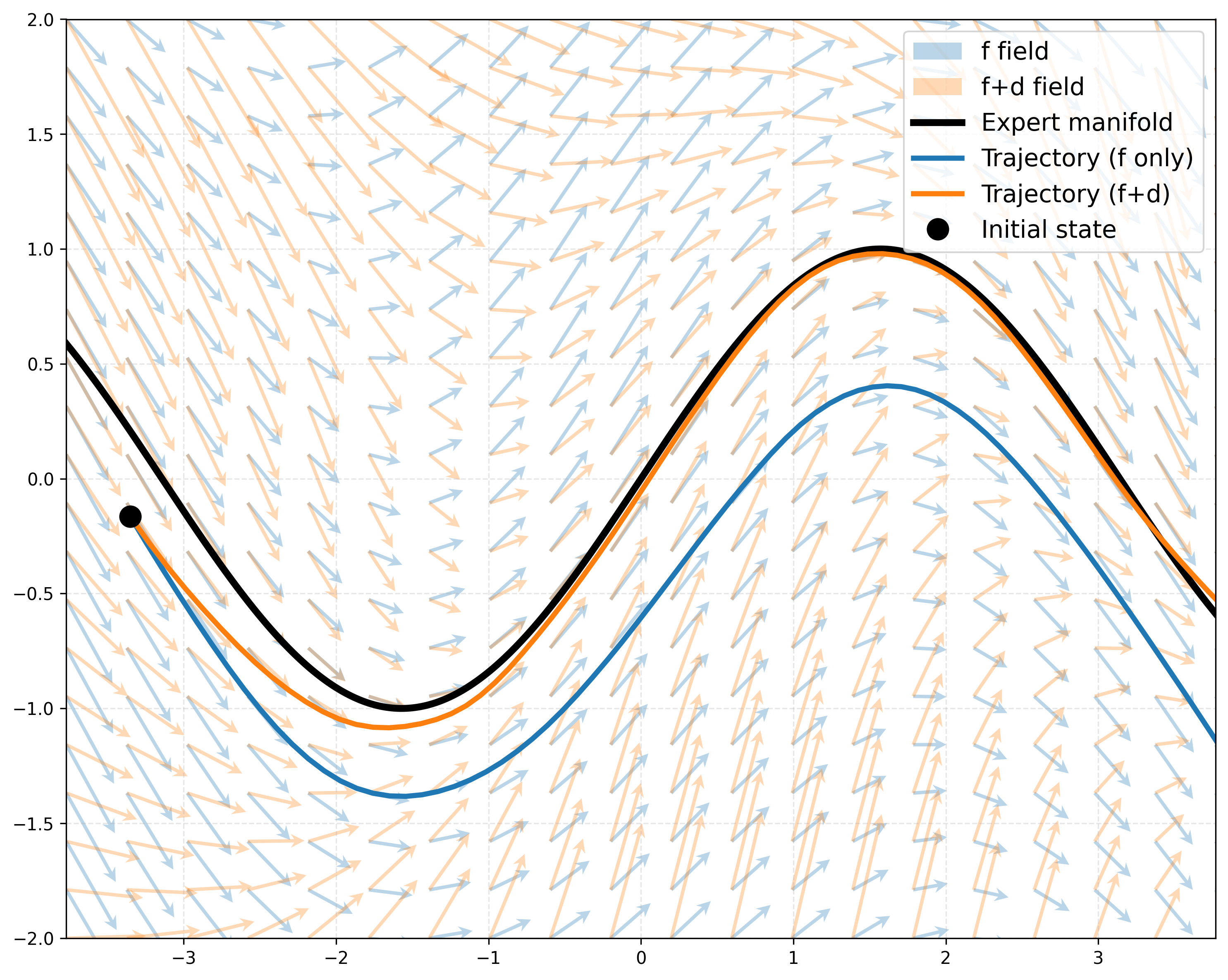
Macheng Shen, Jishen Peng, Zefang Huang
A fundamental challenge in imitation learning is the covariate shift problem.
Existing methods to mitigate covariate shift often require additional expert interactions,
access to environment dynamics, or complex adversarial training, which may not be practical in
real-world applications. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective method (DeCIL) to
mitigate covariate shift by incorporating a denoising mechanism that enhances the contraction
properties of the state transition mapping. Our approach involves training two neural networks:
a dynamics model ( f ) that predicts the next state from the current state, and a joint
state-action denoising policy network ( d ) that refines this state prediction via denoising and
outputs the corresponding action. We provide theoretical analysis showing that the denoising
network acts as a local contraction mapping, reducing the error propagation of the state
transition and improving stability. Our method is straightforward to implement and can be easily
integrated with existing imitation learning frameworks without requiring additional expert data
or complex modifications to the training procedure. Empirical results demonstrate that our
approach effectively improves success rate of various imitation learning tasks under noise
perturbation.
|
|
|
|
Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Ph.D student in Control Science and Engineering • Sep. 2025 to Present |
 |
|
Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
B.E. in Computer Science and Technology • Sep. 2021 to Jun. 2025 |
 |